


In the case where the events are mutually exclusive, the calculation of the probability is simpler:Ī basic example of mutually exclusive events would be the rolling of a dice, where event A is the probability that an even number is rolled, and event B is the probability that an odd number is rolled. There are two cases for the union of events the events are either mutually exclusive, or the events are not mutually exclusive. This means that while at least one of the conditions within the union must hold true, all conditions can be simultaneously true. In this case, the "inclusive OR" is being used.
Note that P(A U B) can also be written as P(A OR B). In probability, the union of events, P(A U B), essentially involves the condition where any or all of the events being considered occur, shown in the Venn diagram below. Probability of drawing a blue and then black marble using the probabilities calculated above: Thus, if a person wanted to determine the probability of withdrawing a blue and then black marble from the bag: Probability of drawing a black marble given that a blue marble was drawn:Īs can be seen, the probability that a black marble is drawn is affected by any previous event where a black or blue marble was drawn without replacement. Calculate the probability of drawing a black marble if a blue marble has been withdrawn without replacement (the blue marble is removed from the bag, reducing the total number of marbles in the bag): Take the example of a bag of 10 marbles, 7 of which are black, and 3 of which are blue. Calculating the probability is slightly more involved when the events are dependent, and involves an understanding of conditional probability, or the probability of event A given that event B has occurred, P(A|B). The calculator provided considers the case where the probabilities are independent. To find the probability that two separate rolls of a die result in 6 each time: In this case, the probabilities of events A and B are multiplied. Computing P(A ∩ B) is simple if the events are independent. These events would therefore be considered mutually exclusive. Consider the probability of rolling a 4 and 6 on a single roll of a die it is not possible. In the case where A and B are mutually exclusive events, P(A ∩ B) = 0. The intersection of events A and B, written as P(A ∩ B) or P(A AND B) is the joint probability of at least two events, shown below in a Venn diagram. if P(A) = 0.65, P(B) does not necessarily have to equal 0.35, and can equal 0.30 or some other number. Any P(B') would be calculated in the same manner, and it is worth noting that in the calculator above, can be independent i.e. Given this scenario, there is, therefore, a 35% chance that Bob does his homework. If, for example, P(A) = 0.65 represents the probability that Bob does not do his homework, his teacher Sally can predict the probability that Bob does his homework as follows: Given a probability A, denoted by P(A), it is simple to calculate the complement, or the probability that the event described by P(A) does not occur, P(A').
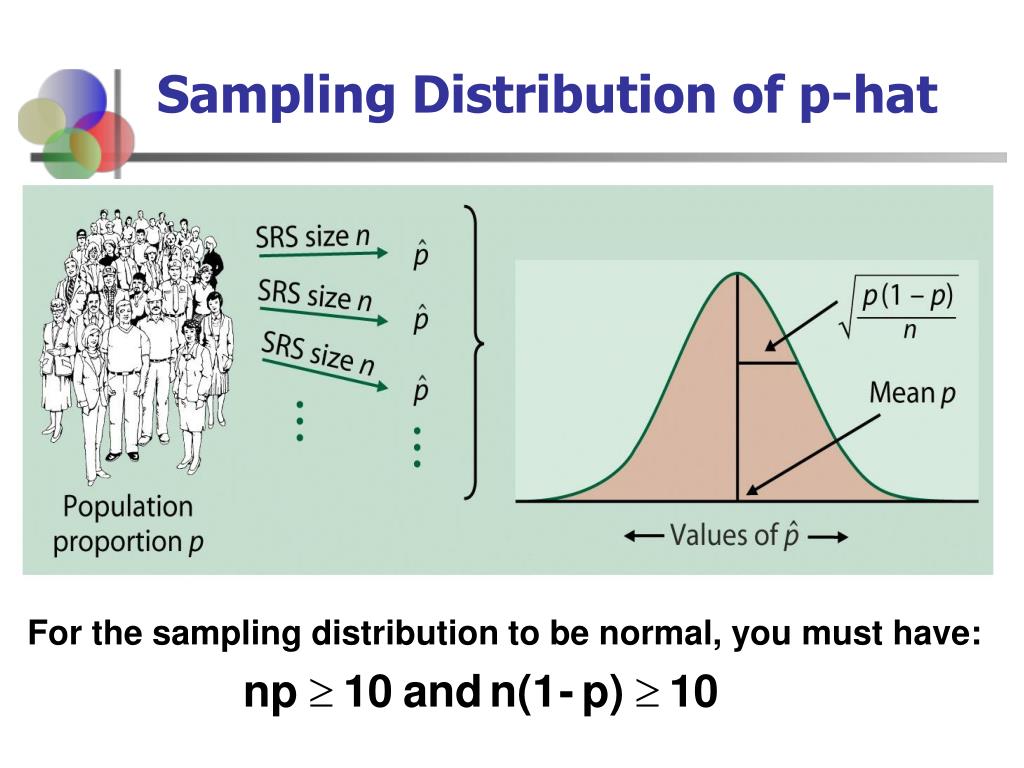
The calculator provided computes the probability that an event A or B does not occur, the probability A and/or B occur when they are not mutually exclusive, the probability that both event A and B occur, and the probability that either event A or event B occurs, but not both. This is further affected by whether the events being studied are independent, mutually exclusive, or conditional, among other things. In its most general case, probability can be defined numerically as the number of desired outcomes divided by the total number of outcomes. It follows that the higher the probability of an event, the more certain it is that the event will occur. It is quantified as a number between 0 and 1, with 1 signifying certainty, and 0 signifying that the event cannot occur. Probability is the measure of the likelihood of an event occurring. Related Standard Deviation Calculator | Sample Size Calculator | Statistics Calculator Use the calculator below to find the area P shown in the normal distribution, as well as the confidence intervals for a range of confidence levels.
#Finding p hat of two stats stat crunch series
Probability of a Series of Independent Events


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
